Inadequate compensation for lost or downgraded protected areas threatens global biodiversity
October 01, 2024Conservation scientists at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have highlighted substantial gaps in the compensation for lost or downgraded protected areas. These gaps risk undermining global efforts for the protection of biodiversity and threaten the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework targets, which aim to conserve 30% of the planet by 2030.
The importance of protected areas
Protected areas play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity, mitigating climate change, and providing essential ecosystem services. These areas are intended for permanent protection, but since the 1900s, many protected areas have suffered downgrading, downsizing, and degazettement (PADDD) events, which expose previously protected species and ecosystems to extinction risks. Despite efforts to implement PADDD offsets and establish new protected areas, these measures often fail to fully restore lost biodiversity protection that PADDD events caused.
Research findings on PADDD compensation
The study, led by Associate Professor Roman CARRASCO and his Research Associate, Ms YAN Yanyun, both from the Department of Biological Sciences at NUS, reveals a critical shortfall in efforts to compensate for lost or downgraded protected areas via PADDD. The research team used global biodiversity data and spatial modelling to evaluate whether offsets for PADDD events, and newly established, unrelated protected areas effectively restored the integrity of the reserve networks.
The findings have been published in the journal Conservation Biology.
Prof Carrasco said, “Our results demonstrate that the loss of protected areas is not sufficiently compensated by either dedicated offsets or the creation of new protected areas. While there appears to be partial recovery in terms of area, the quality of restoration across biodiversity metrics such as for birds, mammals, amphibians and reptiles remains insufficient.”
Methodology and key insights
The study examined 16 territories (including Alaska, Australia, Bhutan, Brazil, Cambodia, Canada, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Hawaii, Mexico, Peru, South Africa, Uganda, the United Kingdom, and the United States) that experienced terrestrial PADDD events and four marine territories (including Australia, Palau, South Africa, and the United States) affected by PADDD events from 2011 to 2020. The evaluation encompassed compensation metrics such as the size of PADDD offsets, the establishment of new protected areas, and the extent of protection restored in Key Biodiversity Areas, ecoregions, and the ranges of threatened species.
Findings indicated that PADDD offsets were implemented in only 19% of affected terrestrial territories and 25% of marine territories. Considering both PADDD offsets and new protected areas, the restoration of the protection was partial: 63% of PADDD affected terrestrial territories have their lost area compensated, and 57% of these territories have had their Key Biodiversity Areas coverage restored. Restoration based on territories was even lower for ecoregions representation and threatened species, with only 38% in ecoregions, 20% in amphibians, 33% in mammals, 31% in birds, and 21% in reptiles regaining adequate protection.
Urgent need for strategic conservation
Ms Yan said, “There is an urgent need to expand PADDD offsets and new protected areas to ensure biodiversity losses are recovered. This will allow us to meet the 30×30 target set by the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework with a focus on quality, not just quantity of area covered.”
“The results indicate that we are losing high quality protected areas that were critical to conserve numerous species, and we are not providing alternative protections. This leads to a degradation of protection, leaving vulnerable species increasingly exposed,” added Prof Carrasco.
The findings underscore the largely detrimental role of PADDD events and highlight the need for a more strategic approach in maintaining and designing protected area networks. To safeguard global biodiversity, it is important to focus on restoring the quality of protection alongside expanding the quantity of protected areas.
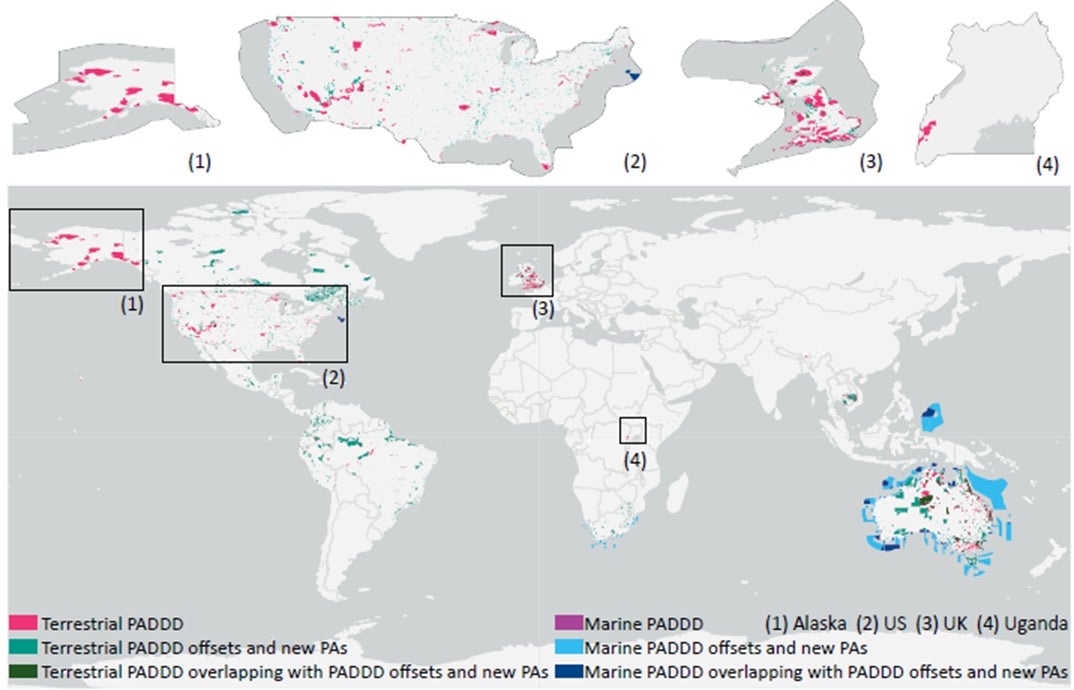
The map shows the locations of terrestrial and marine protected area downgrading, downsizing, and degazettement (PADDD) events across 16 regions from 2011 to 2020. The colour-coded areas represent different types of PADDD events and compensation measures. The overlap of PADDD events and compensation efforts are highlighted in darker shades. The visualisation emphasizes the global scope of PADDD impacts and the uneven application of compensatory actions. [Credit: Conservation Biology]
Reference
Yan Y*; Tan SL; Webb EL; Watson JEM; Carrasco LR*, “Ability of new protected areas to counteract losses from downgrading, downsizing, and degazettement” Conservation Biology, e14381 DOI:10.1111/cobi.14381 Published: 2024.


