Cost-effective patient care clinics
WEE Hwee Lin ((Group Leader, Pharmacy) ) June 08, 20178 Jun 2017. NUS researchers have shown that having pharmacist-managed clinics can provide effective healthcare services at a lower cost.
As Singapore’s demographic patterns change, there is increasing pressure on the national healthcare system to continue providing effective care for patients. Healthcare costs have been rising steadily, due in part to the ageing population and a more sedentary lifestyle. Healthcare organisations are exploring ways to provide a high level of patient care while keeping costs manageable.
NUS researchers conducted a study on the cost-effectiveness of treatment strategies for patients on anticoagulation therapy. Their study found that having Pharmacist-Managed Anticoagulation Clinics (PACCs) is more cost-effective, compared with usual practices. There are improvements in the patients’ conditions, while costs are lowered.
Warfarin is one of the most frequently prescribed oral anticoagulants to thin blood and prevent the formation of harmful blood clots in patients. Although it is an effective drug, different patients respond very differently to warfarin. This complex dose-response relationship makes its safe use a challenge. Patients on warfarin require close monitoring as the dosage required is influenced by many factors such as food, use of other medications and use of alcohol.
In collaboration with the Singapore General Hospital (SGH), Prof WEE Hwee Lin from the Department of Pharmacy, NUS and her students used real-world data and demonstrated that having PACC improves clinical outcomes at a lower cost compared to usual practices under various scenarios. They used the clinical and cost data provided by SGH and data published in scientific literature in their computer simulation study. In one of the scenarios, they found that having the PACC could potentially reduce the patient’s medical expenses by up to S$1,222.67 for a particular group of patients.
Pharmacists are an integral part of the healthcare system and can play a unique role, providing valuable clinical services to manage overall healthcare costs. Although this concept is not new, this is the first local study of this nature for patients on anticoagulation therapy. The findings are similar to other studies conducted in healthcare establishments overseas. Prof Wee says, “We hope that these findings will encourage healthcare practitioners to consider establishing such patient care clinics, to provide cost-effective healthcare services for our patients.”
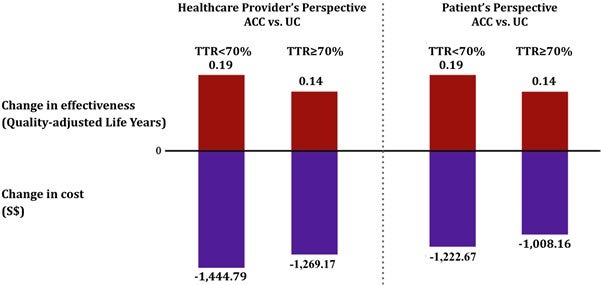
Figure shows the potential change in treatment effectiveness and cost when having PACC. It provides the expected outcomes from both the healthcare provider and patient perspectives for different subgroups based on time in therapeutic range (TTR).
Reference
Chua WBB; Cheen HHM; Kong MC; Chen LL; Wee HL*, “Modelling the cost-effectiveness of pharmacist-managed anticoagulation service for older adults with atrial fibrillation in Singapore” INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PHARMACY Volume: 38 Issue: 5 Pages: 1230-1240 DOI: 10.1007/s11096-016-0357-7 Published: 2016.


